2011 Japan Earthquake Aftermath: significant impacts on Japanese Timber Industry & Logistics... but not critical
Gustavo Iglesias Trabado 
GIT Forestry Consulting SL - Consultoría y Servicios de Ingeniería Agroforestal - www.git-forestry.com - EUCALYPTOLOGICS

GIT Forestry Consulting SL - Consultoría y Servicios de Ingeniería Agroforestal - www.git-forestry.com - EUCALYPTOLOGICS

The devastation caused by the Great Tohoku Earthquake of March 2011 and the subsequent tsunami has impacted both directly and indirectly on many strategic industrial sectors for Japanese economy. Direct impacts have effected the energy sector (up to 30% of total electric power capacity was temporarily limited for security reasons in Japanese nuclear plants and due to damaged infrastructure), which in turn impacts all the other energy dependent sectors. Directly effected also, electronics, technological, siderurgic and automotive industries, which in turn creates impacts on the global distribution chains.
Indirectly impacted, agro-businesses and food supply industries, including fisheries, and their associated industrial transformation chains due to direct damage to their hardware and infrastructures, but indirectly also for food security reasons.

Fig 1: 03/2011 Great Tōhoku Earthquake Summary Map (USGS - United States Geological Survey Service & Global Seismographic Network, March 11th). A larger version is available from USGS (PDF Download).
In what has to do with Japanese forestry related industries, significant impacts have been reported for the majority of sub-sectors, albeit with variable degree and non critical condition for several, or without significant global scale implications in all cases.
Woodchips, Pulp & Paper... and the Rebuilding of Japan
Considering for a moment the case of woodchip, pulp and paper export-imports for the Japanese P&P industry, it is important to take in account that some basic macro-magnitudes, as that Japan imports circa 65% of its yearly annual woodchip consumption, but only a 15% of its yearly consumption of cellulosic pulp is market pulp, and only a 7% of yearly paper consumption is sourced from imports. A quite important amount of these imported woodchips starting the P&P manufacture chain is sourced from countries with significant planted forest resources, especially Eucalyptus planted forests.

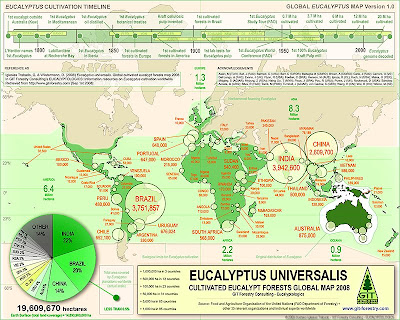
Fig 2: Eucalyptus Planted Forests & their significance for World Forests & Global Timber Supply (2010). A larger version is available from GIT Forestry Consulting upon request (just contact us).
Woodchips, even if important when considered as overall import-export volumes, are not the main fiber source for cellulosic pulp and further paper manufacture in Japan, which normally takes place in integrated mill complexes, some of which have been directly affected by the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami 2011. Japan is one of the countries with a highest rate of paper recycling in the world, which a rapidly advancing paper recovery ratio that has increased from 50% to nearly 80% in just one decade. Recovered paper is the main source instead, supplying beyond 60% of the total brute volume of fiber used in these industrial processes.

Fig 3: 03/2011 Earthquake Impact on Japanese Pulp & Paper Industry: Effected Woodchip Import Flows Map, a preliminary outlook to import-export markets potentially affected (March 21th 21:00 CET). A larger version is available from GIT Forestry Consulting upon request (just contact us).
Given the reported earthquake & tsunami impact to Japanese pulp and paper industry, the temporary cease of operations for some industrial complexes means barely a 10% of the total effective capacity for paper production during the last trienium, which was already not the maximum potential capacity. In addition, damage is not spatially widespread, being restricted just to the most damaged areas in the Northeast of Japan, and it is not either concentrated in a single type of paper production, but spread across several market segments. The strong industry in other areas of the country can reabsorb the temporarily lost productive capacity and is expected to be able to sustain an internal offer enough to appease the normal demand of Japanese citizens.

Fig 4: 14/03/2011 Earthquake Impact on Japanese Pulp & Paper Industry Map, a First Damage Report to Industrial Complexes Effected (March 14th 21:00 CET). A larger version is available from GIT Forestry Consulting upon request (just contact us).
Other timber industry market segments are expected to be more affected in increased import-export value generation term, especially those associated with rebuilding efforts: softwood & hardwood lumber grade logs, crude sawntimber, finished sawntimber & solidwood, and also board, panels & plywood demand is expected to grow steadily in the medium term, especially for those segments in which Japan has increasingly become dependent of external supply even in normal conditions.
Tsunami Damage to Japanese Ports & Impact on Timber Products Logistics
Differently to what was experienced after the 2010 Chilean Earthquake and subsequent tsunami, which hit the core of its pulp and paper industry and paralyzed primary resource and strategic semi-elaborated product exports in the country, including woodchips and market cellulosic pulp for months, damage levels to port infrastructures in Japan do not reach critical thresholds capable of stopping its industrial or economic machinery in the medium term, but yes able to slow its normal production rhythm for several sectors, at least for a time. This different impact is related to the abundance and dispersal of port infrastructures along the Japanese coast, including large industrial and commercial hubs well away of the most effected area.
Majority of Southwestern ports, including the largest ones in the country, can already operate normally, and so can the strategic port complexes in the bays of Tokyo and Chiba. Their temporary cease of activity was cautionary in front of the possibility of further tsunamis caused by major aftershocks, and the levels of damage, albeit significant, are not severe.

Fig 5: 03/2011 Earthquake Impact on Japanese Pulp & Paper Industry: Tsunami Affected Japanese Forest Products Ports & Timber Industry Logistics Map, a preliminary outlook to import-export infrastructures affected (March 21th 21:00 CET). A larger version is available from GIT Forestry Consulting upon request (just contact us).
A different case in Northeastern Japan: one of the large ports most heavily impacted by the 2011 Tsunami is Hachinohe, probably non operative for months. Its major activity range is related to fisheries, oil and petrochemical industries, but a small percent of forestry related input supply has been reported as effected.

Fig 6: 03/2011 Earthquake Impact on Japanese Pulp & Paper Industry: Tsunami Affected Japanese Forest Products Ports: Case Study 03 (March 21th 21:00 CET). A larger version is available from GIT Forestry Consulting upon request (just contact us).
The ports of Sendai, Onahama & Ishinomaki, where tsunami wave height reached ranges within 5 to 10 meters, have been almost totally destroyed after their oceanic defenses were overwhelmed and it is possible they will not manage to operate normally for years. In these ports there is a significant activity associated to timber industries, and among other impacts, besides the destruction of port infrastructures, primary resource and finished product stocks have been reported as lost or heavily damaged, including newspaper, printing paper, cardboard and specialty paper stocks.
A dozen of other ports in this region of Japan, some of which also operate with forestry related products, have also been severely damaged, are no longer operating, will not be operating in the short term and probably will not be operating either in the medium term.
We will try to keep you updated with any available information as soon as possible in GIT Forestry's blog, but you can also reach Eucalyptologics updates via Twitter and Facebook.
UPDATE: DAMAGE REPORT TO JAPANESE PULP & PAPER MILL INDUSTRIAL COMPLEXES AND FOREST PRODUCT PORTS: CASE STUDY 02

Fig 7: 03/2011 Great Tōhoku Earthquake & Tsunami Impact on Japanese Pulp & Paper Industry: Tsunami Affected Japanese Pulp & Paper Mills and Forest Products Ports: Case Study 02 - NPG (March 29th 08:00 CET). A Giant Size High Detail version able to be printed in sizes up to 400 x 200 cm is available from GIT Forestry Consulting upon request (just contact us).
"Don't give up the hope"
Also at EUCALYPTOLOGICS...




Want to contact us?

Contact GIT Forestry Consulting - Eucalyptologics

GIT's Eucalyptology Topics
© 2007-2011 Gustavo Iglesias Trabado & Associates. Please contact us if you want to use all or part of this text and photography elsewhere. We like to share, but we do not like rudeness.

superb!
ReplyDeleteYou have a nice blog
ReplyDeleteBramco Engineers: New range of pulp and paper mil machines